About H-2A
The H-2A nonimmigrant visa program allows employers to hire foreign workers for temporary agricultural jobs when they cannot find enough U.S. workers.
Employers must apply for permission from the U.S. government to hire foreign individuals as H-2A nonimmigrants. They can hire non-U.S. citizens as long as the wages and working conditions of U.S. workers are not adversely affected by the employment of foreign workers. After the approved work period ends, the worker must leave the United States. An H-2A visa only permits temporary agricultural work for a specific employer for a fixed period, less than one year. There is no annual limit of H-2A visas available each fiscal year. In 2024, the U.S. Department of State issued 315,328 H-2A visas, nearly quadruple the number issued ten years prior (89,274 in 2014). The H-2A visa does not offer the workers a path to lawful permanent residence or citizenship.
Typical H-2A Occupations
Crop Workers
Common H-2A jobs include tending to tobacco; pruning and picking fruit; planting and harvesting vegetable row crops; and working in nurseries and greenhouses.
Herders
H-2A workers are also contracted to work on cattle ranches and herding sheep.
Worker Protections
The H-2A program includes many worker protections to ensure fair and safe conditions, affecting contracts, wages, housing, and transportation. However, those rules and the required oversight are often criticized as inadequate to ensure worker protection.
Wages: Employers must offer H-2A workers a Department of Labor (DOL) set wage rate and payment must be made at least every two weeks.
Housing: Employers must provide safe and clean housing for H-2A workers at no cost.
Transportation Costs: H-2A workers are entitled to inbound and outbound transportation costs between their homes and the worksite.
Contract: Before H-2A workers arrive in the United States, employers must provide a job-specific contract detailing the terms and conditions of employment, written in a language the worker understands. This contract must describe job duties, wages, work hours, and other relevant provisions.
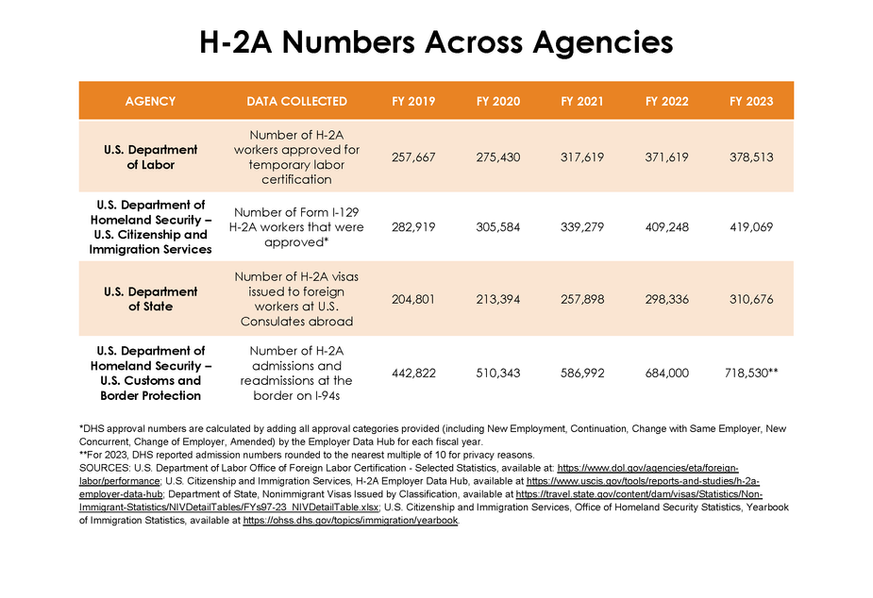
H-2A by the Numbers
Issues
Labor Abuse
Illegal Recruitment Fees: H-2A workers often rely on labor contractors or recruiters to connect them with job opportunities in the United States. It is far too common that these contractors and recruiters charge workers illegal recruitment fees. These fees can leave workers in debt and vulnerable to exploitation.
Breach of Contract: Additionally, many H-2A workers have claimed that employers pay less than promised wages, change the agreed-upon terms and conditions of employment, and require them to work in unsafe conditions.
Documented Cases of Abuse
Camayo v. Peroulis and Sons Sheep, Inc.
Plaintiffs Camayo and Damian, sheepherders from the highlands of Peru, were brought to the U.S. under the H-2A visa guest worker program to work for Defendants, Louis Peroulis, Stanley Peroulis, Crisologo Damian, and John Peroulis & Sons Sheep, Inc., and were subject to forced labor, abuse, and trafficking in violation of the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act, along with state-law violations. Defendants are an agricultural company in Colorado. As a condition of the job, Plaintiffs had to pay several non-recruitment fees to banks and offices in Peru for their paperwork. Around March to June 2009, Plaintiffs arrived in Colorado, and were immediately put to work. Defendants told Plaintiffs that their employment would last 3 years. Defendants had a complex system of control on the ranch where Plaintiffs worked: Defendants confiscated their passports, restricted them from such minimal provisions that they often went hungry because they did not have enough food. Additionally, Defendants Stanley and Louis Peroulis repeatedly verbally abused Plaintiffs by calling them racial epithets. Defendants, in fact, have a history of mistreating workers—the U.S. DOL had previously investigated and filed a case against them. Moreover, Defendants would control Plaintiffs by threatening to deport them if they did not continue to work. Eventually, Plaintiffs filed a complaint in the federal district court, in the District of Colorado. On October 29, 2013, the court closed the case after the parties settled out of court.
Gutierrez-Morales v. Planck
Plaintiffs, 9 Mexican H-2A farmworkers, were recruited, hired, employed, and housed by Defendants to perform agricultural work in tobacco during the 2013-2014 and 2014-2015 seasons, and were subjected to forced labor, involuntary servitude, and wage exploitation in violation of the Fair Labor Standards Act, the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act, and state-law contract law. Defendants began participating in the H-2A visa program in 2013 or 2014, seeking to bring Mexican workers to work as laborers at their tobacco farms in or around Nicolas County, Kentucky. Defendants lured Plaintiffs to the United States with fraudulent promises of good working and living conditions at a fair wage. Throughout the course of Plaintiffs’ employment in the 2013-2014 and 2014-2015 tobacco seasons, Defendants repeatedly disregarded the promises they had made to the Plaintiffs and the federal government, and instead violated Plaintiffs’ rights under both federal law and the terms of their work contracts. Defendants paid Plaintiffs at an hourly rate well below what they had promised, made illegal deductions from their pay, and failed to maintain accurate records of Plaintiffs’ hours, causing Plaintiffs to earn well below the promised contract wage and even less than the federal Fair Labor Standards Act (“FLSA”) minimum wage of $7.25 per hour. Defendants housed Plaintiffs in sub-standard facilities, exposing them to unsanitary and inhumane living conditions. Defendants unlawfully confiscated Plaintiffs’ passports and other personal documents in an attempt to prevent Plaintiffs from leaving their employment before the end of the season. Eventually, Plaintiffs filed a complaint in the federal district court, in the Eastern District of Kentucky. On March 7, 2017, after a settlement was reached, the court closed the case.
USA v. Patricio et al. (Operation Blooming Onion)
Two dozen defendants were indicted on 54 charges as a result of an investigation into a visa fraud and labor trafficking operation that illegally imported Mexican and Central American workers into brutal conditions on South Georgia farms. Since at least 2015, the defendants used the H-2A work visa program to bring temporary foreign workers from Mexico, Guatemala, and Honduras into the United States to labor as agricultural workers. Defendants obligated the workers to pay prohibited travel, food, and housing fees while illegally confiscating personal identification documents. The workers engaged in strenuous and difficult work while ultimately receiving little or no pay. The victims were housed by their traffickers in crowded, filthy living conditions, but were kept compliant with threats of deportation and violence. The traffickers made more than $200 million through their exploitation of workers, laundering the funds through cash purchases of land, homes, vehicles, and businesses, and by funneling millions of dollars through a casino. The more than 200 workers were required to dig onions with their bare hands while receiving a mere 20 cents for each bucket harvested. Workers were held in fenced work camps, given inadequate food, had access to limited plumbing, and often no drinking water. The defendants threatened the workers with weapons and violence and also resorted to raping, kidnapping, and threatening or attempting to kill some of the workers’ families. Two workers died as a result of the defendants’ mistreatment. In early 2024, nearly half of the defendants pleaded guilty to the charges against them.
Lack of effective oversight, limited enforcement of program rules and general labor law, and often unavailable access to legal remedies increase the vulnerability of H-2A workers. Addressing these aws in the H-2A program needs a comprehensive approach that enhances enforcement, improves oversight, eliminates recruitment fees, and provides access to legal remedies when there is abuse.
Recommendations
Transparency
Data Reporting: Congress should create a uniform system for reporting data that the federal government already collects on temporary visa programs and require that information be made publicly available. This information would give the government and advocates the data they need to comprehensively analyze visa programs like the H-2A visa for systemic abuse and identify potential victims of trafficking and forced labor.
Contracting and Recruiting Arrangements: Congress should authorize the Department of Labor (DOL) to require H-2A employers to disclose all arrangements with and identities of H-2A Labor Contractors (H-2ALCs) and foreign labor recruiters and disclose all contracting and recruiting in foreign countries, including by sub-contractors and sub-agents.
Registered Agent List: DOL should maintain and publish a list of all registered agents and their relationships.
Fair Recruitment
The H-2A program needs increased regulation of the recruitment of H-2A workers to protect against fraud, discrimination, and human trafficking. To improve safe recruitment for workers, Congress should require employers to hire registered foreign labor contractors and to hold those registered contractors liable for seeking or collecting prohibited fees from workers seeking H-2A employment.
Effective Oversight
Enforce Laws: Congress should allocate more funds to the DOL, the Department of Homeland Security, and the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission to enforce laws and regulations governing the H-2A program.
Worksite Inspections: Those agencies should have dedicated, highly trained staff to pursue investigations and inspections into potential exploitation and violations. There should be enough investigators to conduct a statistically significant sample of random inspections at H-2A worksites to detect and ultimately dissuade noncompliance by H-2A employers.